内核基数树
Linux 内核学习笔记系列,GCC 扩展语法和内核数据结构部分,简单介绍 Linux 内核基数树。
基数树简介
前缀树(字典树)
该部分内容来源于维基百科。
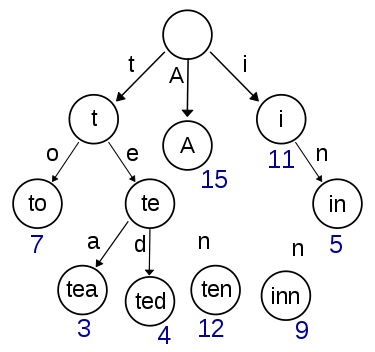
在计算机科学中,trie,又称前缀树或字典树,是一种有序树,用于保存关联数组,其中的键通常是字符串。与二叉查找树不同,键不是直接保存在节点中,而是由节点在树中的位置决定。一个节点的所有子孙都有相同的前缀,也就是这个节点对应的字符串,而根节点对应空字符串。一般情况下,不是所有的节点都有对应的值,只有叶子节点和部分内部节点所对应的键才有相关的值。
在图示中,键标注在节点中,值标注在节点之下。每一个完整的英文单词对应一个特定的整数。Trie可以看作是一个确定有限状态自动机,尽管边上的符号一般是隐含在分支的顺序中的。
键不需要被显式地保存在节点中。图示中标注出完整的单词,只是为了演示trie的原理。
trie中的键通常是字符串,但也可以是其它的结构。trie的算法可以很容易地修改为处理其它结构的有序序列,比如一串数字或者形状的排列。比如,bitwise trie中的键是一串比特,可以用于表示整数或者内存地址。
基数树
该部分内容来源于维基百科。
在计算机科学中,基数树(也叫基数特里树或压缩前缀树)是一种数据结构,是一种更节省空间的Trie(前缀树),其中作为唯一子节点的每个节点都与其父节点合并,边既可以表示为元素序列又可以表示为单个元素。因此每个内部节点的子节点数最多为基数树的基数r ,其中r为正整数,x为2的幂,x≥1,这使得基数树更适用于对于较小的集合(尤其是字符串很长的情况下)和有很长相同前缀的字符串集合。
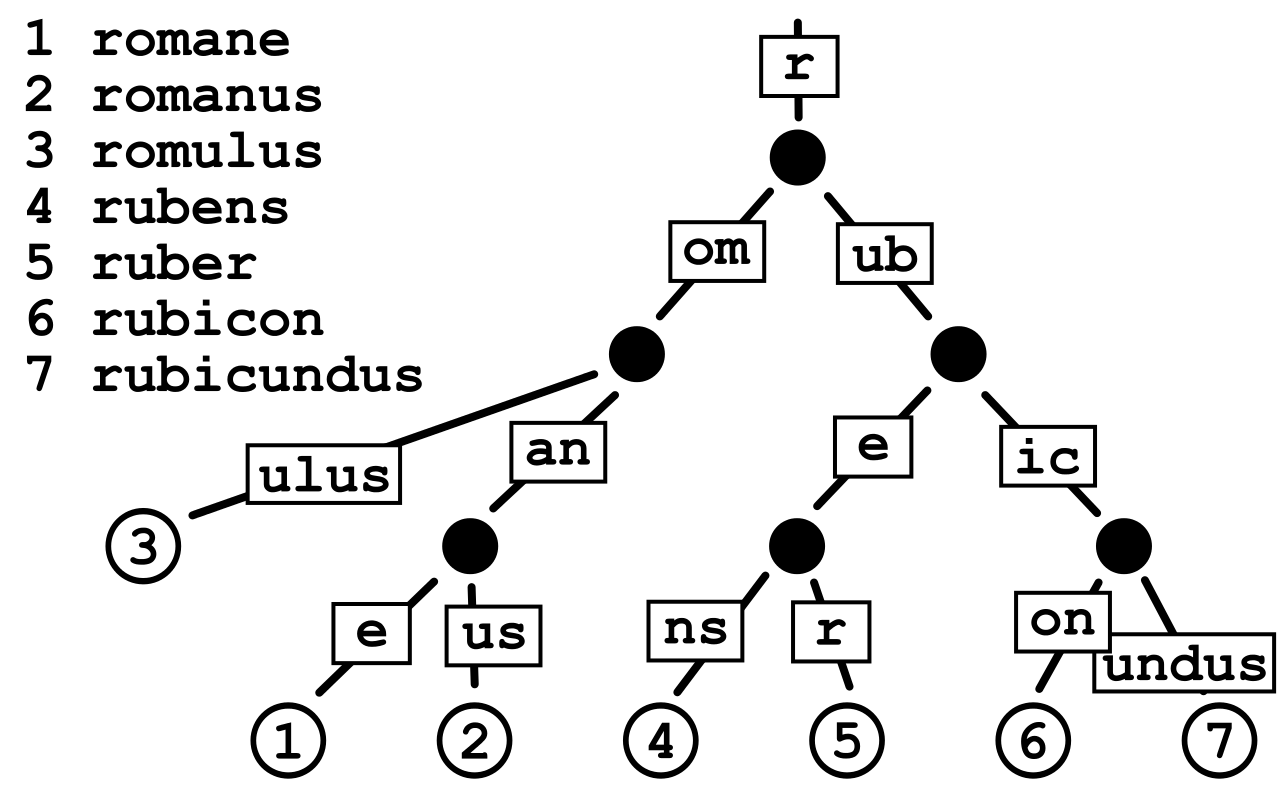
基数树支持插入、删除、查找操作。查找包括完全匹配、前缀匹配、前驱查找、后继查找。所有这些操作都是O(k)复杂度,其中k是所有字符串中最大的长度。
内核基数树的使用
内核红黑树的实现称为 radix_tree,头文件为 include/linux/radix-tree.h。下面只介绍几个基本的 API 和相关实现。
基数树的创建
最简单的方式,直接使用宏创建:
RADIX_TREE(name, gfp_mask);
或者,也可以手工创建:
struct radix_tree_root tree;
INIT_RADIX_TREE(&tree, gfp_mask);
基数树的查找
void *radix_tree_lookup(struct radix_tree_root *root, unsigned long index);
该函数在以 root 为根的基数树中查找索引为 index 的内容,返回查找的内容的地址(没找到要查找的内容则返回 NULL)。
unsigned int radix_tree_gang_lookup(struct radix_tree_root *root, void **results, unsigned long first_index, unsigned int max_items);
该函数在以 root 为根的基数树中查找非空内容,从索引为 first_index 的结点开始,最多查找 max_items 个非空内容,查找结果放 results 中,返回找到的个数。
基数树的插入
int radix_tree_insert(struct radix_tree_root *root, unsigned long index, void *item);
该函数将内容 item 插入到以 root 为根的基数树中索引为 index 的地方,插入成功返回 0,失败返回错误值。
基数树的删除
void *radix_tree_delete(struct radix_tree_root *root, unsigned long index);
该函数将索引为 index 的内容从以 root 为根的基数树中删除,返回删除的内容的地址(要删除的内容不存在则返回 NULL)。
内核基数树的的实现
内核基数树的实现均位于 lib/radix-tree.c 和 include/linux/radix-tree.h。我只求会用 API,具体实现的原理要参考数据结构书籍,下面也只贴出部分核心代码。
基数树的定义
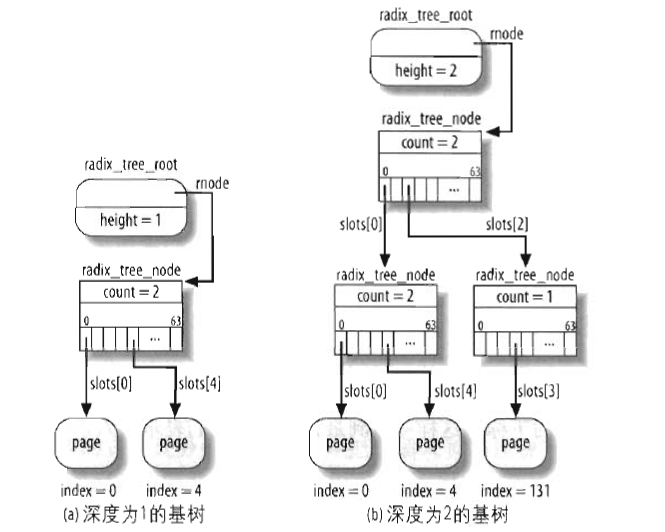
根的定义如下:
/* root tags are stored in gfp_mask, shifted by __GFP_BITS_SHIFT */
struct radix_tree_root {
unsigned int height;
gfp_t gfp_mask;
struct radix_tree_node *rnode;
};
结点的定义如下:
#define RADIX_TREE_MAX_TAGS 2
#ifdef __KERNEL__
#define RADIX_TREE_MAP_SHIFT (CONFIG_BASE_SMALL ? 4 : 6)
#else
#define RADIX_TREE_MAP_SHIFT 3 /* For more stressful testing */
#endif
#define RADIX_TREE_MAP_SIZE (1UL << RADIX_TREE_MAP_SHIFT)
#define RADIX_TREE_TAG_LONGS \
((RADIX_TREE_MAP_SIZE + BITS_PER_LONG - 1) / BITS_PER_LONG)
struct radix_tree_node {
unsigned int height; /* Height from the bottom */
unsigned int count;
struct rcu_head rcu_head;
void *slots[RADIX_TREE_MAP_SIZE];
unsigned long tags[RADIX_TREE_MAX_TAGS][RADIX_TREE_TAG_LONGS];
};
其中,BITS_PER_LONG 是体系结构相关的,指该体系结构下 long 占多少位,该宏在 32 位系统下通常是 32,64 位系统下通常是 64。
基数树创建的实现
#define RADIX_TREE_INIT(mask) { \
.height = 0, \
.gfp_mask = (mask), \
.rnode = NULL, \
}
#define RADIX_TREE(name, mask) \
struct radix_tree_root name = RADIX_TREE_INIT(mask)
#define INIT_RADIX_TREE(root, mask) \
do { \
(root)->height = 0; \
(root)->gfp_mask = (mask); \
(root)->rnode = NULL; \
} while (0)
辅助函数/宏的实现
#define RADIX_TREE_INDIRECT_PTR 1
static inline void *radix_tree_indirect_to_ptr(void *ptr)
{
return (void *)((unsigned long)ptr & ~RADIX_TREE_INDIRECT_PTR);
}
static inline int radix_tree_is_indirect_ptr(void *ptr)
{
return (int)((unsigned long)ptr & RADIX_TREE_INDIRECT_PTR);
}
/*
* Return the maximum key which can be store into a
* radix tree with height HEIGHT.
*/
static inline unsigned long radix_tree_maxindex(unsigned int height)
{
return height_to_maxindex[height];
}
对于前两个函数,由于地址总是对齐的,不管哪种体系结构,地址的最后一位总是 0。所以可以利用这一位,存储该结点是直接结点(指针直接指向内容)还是间接结点(指针指向其他树的结点)。
基数树的查找的实现
#define RADIX_TREE_MAP_MASK (RADIX_TREE_MAP_SIZE-1)
/*
* is_slot == 1 : search for the slot.
* is_slot == 0 : search for the node.
*/
static void *radix_tree_lookup_element(struct radix_tree_root *root,
unsigned long index, int is_slot)
{
unsigned int height, shift;
struct radix_tree_node *node, **slot;
node = rcu_dereference_raw(root->rnode);
if (node == NULL)
return NULL;
if (!radix_tree_is_indirect_ptr(node)) {
if (index > 0)
return NULL;
return is_slot ? (void *)&root->rnode : node;
}
node = radix_tree_indirect_to_ptr(node);
height = node->height;
if (index > radix_tree_maxindex(height))
return NULL;
shift = (height-1) * RADIX_TREE_MAP_SHIFT;
do {
slot = (struct radix_tree_node **)
(node->slots + ((index>>shift) & RADIX_TREE_MAP_MASK));
node = rcu_dereference_raw(*slot);
if (node == NULL)
return NULL;
shift -= RADIX_TREE_MAP_SHIFT;
height--;
} while (height > 0);
return is_slot ? (void *)slot:node;
}
/**
* radix_tree_lookup - perform lookup operation on a radix tree
* @root: radix tree root
* @index: index key
*
* Lookup the item at the position @index in the radix tree @root.
*
* This function can be called under rcu_read_lock, however the caller
* must manage lifetimes of leaf nodes (eg. RCU may also be used to free
* them safely). No RCU barriers are required to access or modify the
* returned item, however.
*/
void *radix_tree_lookup(struct radix_tree_root *root, unsigned long index)
{
return radix_tree_lookup_element(root, index, 0);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(radix_tree_lookup);
radix_tree_lookup() 用于查找单个内容,RCU 相关的内容还没看,这里先无视(见 TODO 列表)。
static unsigned int
__lookup(struct radix_tree_node *slot, void ***results, unsigned long index,
unsigned int max_items, unsigned long *next_index)
{
unsigned int nr_found = 0;
unsigned int shift, height;
unsigned long i;
height = slot->height;
if (height == 0)
goto out;
shift = (height-1) * RADIX_TREE_MAP_SHIFT;
for ( ; height > 1; height--) {
i = (index >> shift) & RADIX_TREE_MAP_MASK;
for (;;) {
if (slot->slots[i] != NULL)
break;
index &= ~((1UL << shift) - 1);
index += 1UL << shift;
if (index == 0)
goto out; /* 32-bit wraparound */
i++;
if (i == RADIX_TREE_MAP_SIZE)
goto out;
}
shift -= RADIX_TREE_MAP_SHIFT;
slot = rcu_dereference_raw(slot->slots[i]);
if (slot == NULL)
goto out;
}
/* Bottom level: grab some items */
for (i = index & RADIX_TREE_MAP_MASK; i < RADIX_TREE_MAP_SIZE; i++) {
index++;
if (slot->slots[i]) {
results[nr_found++] = &(slot->slots[i]);
if (nr_found == max_items)
goto out;
}
}
out:
*next_index = index;
return nr_found;
}
/**
* radix_tree_gang_lookup - perform multiple lookup on a radix tree
* @root: radix tree root
* @results: where the results of the lookup are placed
* @first_index: start the lookup from this key
* @max_items: place up to this many items at *results
*
* Performs an index-ascending scan of the tree for present items. Places
* them at *@results and returns the number of items which were placed at
* *@results.
*
* The implementation is naive.
*
* Like radix_tree_lookup, radix_tree_gang_lookup may be called under
* rcu_read_lock. In this case, rather than the returned results being
* an atomic snapshot of the tree at a single point in time, the semantics
* of an RCU protected gang lookup are as though multiple radix_tree_lookups
* have been issued in individual locks, and results stored in 'results'.
*/
unsigned int
radix_tree_gang_lookup(struct radix_tree_root *root, void **results,
unsigned long first_index, unsigned int max_items)
{
unsigned long max_index;
struct radix_tree_node *node;
unsigned long cur_index = first_index;
unsigned int ret;
node = rcu_dereference_raw(root->rnode);
if (!node)
return 0;
if (!radix_tree_is_indirect_ptr(node)) {
if (first_index > 0)
return 0;
results[0] = node;
return 1;
}
node = radix_tree_indirect_to_ptr(node);
max_index = radix_tree_maxindex(node->height);
ret = 0;
while (ret < max_items) {
unsigned int nr_found, slots_found, i;
unsigned long next_index; /* Index of next search */
if (cur_index > max_index)
break;
slots_found = __lookup(node, (void ***)results + ret, cur_index,
max_items - ret, &next_index);
nr_found = 0;
for (i = 0; i < slots_found; i++) {
struct radix_tree_node *slot;
slot = *(((void ***)results)[ret + i]);
if (!slot)
continue;
results[ret + nr_found] = rcu_dereference_raw(slot);
nr_found++;
}
ret += nr_found;
if (next_index == 0)
break;
cur_index = next_index;
}
return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(radix_tree_gang_lookup);
radix_tree_gang_lookup() 用于查找多个内容。
其他查找函数都是同理,只是查找的东西,比如查找 slot 和 tag 等。
基数树的插入的实现
static inline gfp_t root_gfp_mask(struct radix_tree_root *root)
{
return root->gfp_mask & __GFP_BITS_MASK;
}
/*
* This assumes that the caller has performed appropriate preallocation, and
* that the caller has pinned this thread of control to the current CPU.
*/
static struct radix_tree_node *
radix_tree_node_alloc(struct radix_tree_root *root)
{
struct radix_tree_node *ret = NULL;
gfp_t gfp_mask = root_gfp_mask(root);
if (!(gfp_mask & __GFP_WAIT)) {
struct radix_tree_preload *rtp;
/*
* Provided the caller has preloaded here, we will always
* succeed in getting a node here (and never reach
* kmem_cache_alloc)
*/
rtp = &__get_cpu_var(radix_tree_preloads);
if (rtp->nr) {
ret = rtp->nodes[rtp->nr - 1];
rtp->nodes[rtp->nr - 1] = NULL;
rtp->nr--;
}
}
if (ret == NULL)
ret = kmem_cache_alloc(radix_tree_node_cachep, gfp_mask);
BUG_ON(radix_tree_is_indirect_ptr(ret));
return ret;
}
/*
* Extend a radix tree so it can store key @index.
*/
static int radix_tree_extend(struct radix_tree_root *root, unsigned long index)
{
struct radix_tree_node *node;
unsigned int height;
int tag;
/* Figure out what the height should be. */
height = root->height + 1;
while (index > radix_tree_maxindex(height))
height++;
if (root->rnode == NULL) {
root->height = height;
goto out;
}
do {
unsigned int newheight;
if (!(node = radix_tree_node_alloc(root)))
return -ENOMEM;
/* Increase the height. */
node->slots[0] = radix_tree_indirect_to_ptr(root->rnode);
/* Propagate the aggregated tag info into the new root */
for (tag = 0; tag < RADIX_TREE_MAX_TAGS; tag++) {
if (root_tag_get(root, tag))
tag_set(node, tag, 0);
}
newheight = root->height+1;
node->height = newheight;
node->count = 1;
node = radix_tree_ptr_to_indirect(node);
rcu_assign_pointer(root->rnode, node);
root->height = newheight;
} while (height > root->height);
out:
return 0;
}
/**
* radix_tree_insert - insert into a radix tree
* @root: radix tree root
* @index: index key
* @item: item to insert
*
* Insert an item into the radix tree at position @index.
*/
int radix_tree_insert(struct radix_tree_root *root,
unsigned long index, void *item)
{
struct radix_tree_node *node = NULL, *slot;
unsigned int height, shift;
int offset;
int error;
BUG_ON(radix_tree_is_indirect_ptr(item));
/* Make sure the tree is high enough. */
if (index > radix_tree_maxindex(root->height)) {
error = radix_tree_extend(root, index);
if (error)
return error;
}
slot = radix_tree_indirect_to_ptr(root->rnode);
height = root->height;
shift = (height-1) * RADIX_TREE_MAP_SHIFT;
offset = 0; /* uninitialised var warning */
while (height > 0) {
if (slot == NULL) {
/* Have to add a child node. */
if (!(slot = radix_tree_node_alloc(root)))
return -ENOMEM;
slot->height = height;
if (node) {
rcu_assign_pointer(node->slots[offset], slot);
node->count++;
} else
rcu_assign_pointer(root->rnode,
radix_tree_ptr_to_indirect(slot));
}
/* Go a level down */
offset = (index >> shift) & RADIX_TREE_MAP_MASK;
node = slot;
slot = node->slots[offset];
shift -= RADIX_TREE_MAP_SHIFT;
height--;
}
if (slot != NULL)
return -EEXIST;
if (node) {
node->count++;
rcu_assign_pointer(node->slots[offset], item);
BUG_ON(tag_get(node, 0, offset));
BUG_ON(tag_get(node, 1, offset));
} else {
rcu_assign_pointer(root->rnode, item);
BUG_ON(root_tag_get(root, 0));
BUG_ON(root_tag_get(root, 1));
}
return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(radix_tree_insert);
基数树的删除的实现
/**
* radix_tree_shrink - shrink height of a radix tree to minimal
* @root radix tree root
*/
static inline void radix_tree_shrink(struct radix_tree_root *root)
{
/* try to shrink tree height */
while (root->height > 0) {
struct radix_tree_node *to_free = root->rnode;
void *newptr;
BUG_ON(!radix_tree_is_indirect_ptr(to_free));
to_free = radix_tree_indirect_to_ptr(to_free);
/*
* The candidate node has more than one child, or its child
* is not at the leftmost slot, we cannot shrink.
*/
if (to_free->count != 1)
break;
if (!to_free->slots[0])
break;
/*
* We don't need rcu_assign_pointer(), since we are simply
* moving the node from one part of the tree to another. If
* it was safe to dereference the old pointer to it
* (to_free->slots[0]), it will be safe to dereference the new
* one (root->rnode).
*/
newptr = to_free->slots[0];
if (root->height > 1)
newptr = radix_tree_ptr_to_indirect(newptr);
root->rnode = newptr;
root->height--;
radix_tree_node_free(to_free);
}
}
static inline void
radix_tree_node_free(struct radix_tree_node *node)
{
call_rcu(&node->rcu_head, radix_tree_node_rcu_free);
}
/**
* radix_tree_delete - delete an item from a radix tree
* @root: radix tree root
* @index: index key
*
* Remove the item at @index from the radix tree rooted at @root.
*
* Returns the address of the deleted item, or NULL if it was not present.
*/
void *radix_tree_delete(struct radix_tree_root *root, unsigned long index)
{
/*
* The radix tree path needs to be one longer than the maximum path
* since the "list" is null terminated.
*/
struct radix_tree_path path[RADIX_TREE_MAX_PATH + 1], *pathp = path;
struct radix_tree_node *slot = NULL;
struct radix_tree_node *to_free;
unsigned int height, shift;
int tag;
int offset;
height = root->height;
if (index > radix_tree_maxindex(height))
goto out;
slot = root->rnode;
if (height == 0) {
root_tag_clear_all(root);
root->rnode = NULL;
goto out;
}
slot = radix_tree_indirect_to_ptr(slot);
shift = (height - 1) * RADIX_TREE_MAP_SHIFT;
pathp->node = NULL;
do {
if (slot == NULL)
goto out;
pathp++;
offset = (index >> shift) & RADIX_TREE_MAP_MASK;
pathp->offset = offset;
pathp->node = slot;
slot = slot->slots[offset];
shift -= RADIX_TREE_MAP_SHIFT;
height--;
} while (height > 0);
if (slot == NULL)
goto out;
/*
* Clear all tags associated with the just-deleted item
*/
for (tag = 0; tag < RADIX_TREE_MAX_TAGS; tag++) {
if (tag_get(pathp->node, tag, pathp->offset))
radix_tree_tag_clear(root, index, tag);
}
to_free = NULL;
/* Now free the nodes we do not need anymore */
while (pathp->node) {
pathp->node->slots[pathp->offset] = NULL;
pathp->node->count--;
/*
* Queue the node for deferred freeing after the
* last reference to it disappears (set NULL, above).
*/
if (to_free)
radix_tree_node_free(to_free);
if (pathp->node->count) {
if (pathp->node ==
radix_tree_indirect_to_ptr(root->rnode))
radix_tree_shrink(root);
goto out;
}
/* Node with zero slots in use so free it */
to_free = pathp->node;
pathp--;
}
root_tag_clear_all(root);
root->height = 0;
root->rnode = NULL;
if (to_free)
radix_tree_node_free(to_free);
out:
return slot;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(radix_tree_delete);
